Bending of a cantilever beam
In this tutorial, the bending of a cantilever beam is simulated.
A cantilever is a rigid structure that extends horizontally and is unsupported at one end 1. It is widely used in construction and serves as a baseline simulation for structural mechanics.
Model definition
Section titled “Model definition”The model comprises a small aluminium beam built from a single box element. The beam is clamped from one of its end surfaces, and extends horizontally like a flagpole attached to a wall.
A load is evenly applied to the top surface of the beam, bending it downwards. The maximum Z-displacement is solved during simulation.
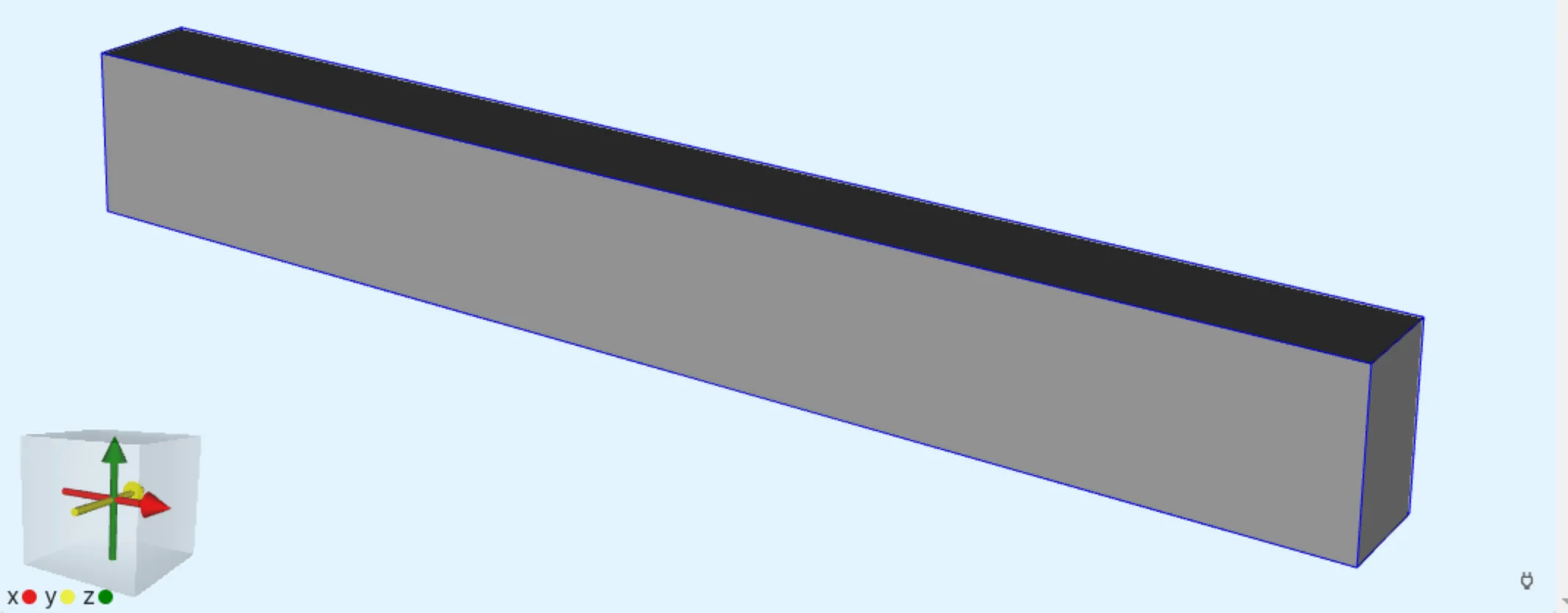
Model geometry
Section titled “Model geometry”| Name | Element type | XYZ dimensions [mm] |
|---|---|---|
| Cantilever beam | Box | 24 x 2 x 3 |
Material Data
Section titled “Material Data”Aluminium
Section titled “Aluminium”| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.32 |
| Young’s modulus [Pa] | 68e9 |
Boundary conditions
Section titled “Boundary conditions”| Name | Type | Value [X, Y, Z] |
|---|---|---|
| left X-plane | Clamp | [0, 0, 0] |
| top Z-plane | Load [N] | [0, 0, -1000] |
Output Results
Section titled “Output Results”Maximum Z-displacement.
Step-by-step guide
Section titled “Step-by-step guide”Below, you’ll find a detailed step-by-step tutorial on how to set up a cantilever beam simulation in Quanscient Allsolve.
Step 1 - Build the geometry
Section titled “Step 1 - Build the geometry”-
Start with a new project and name it
Cantilever beam. -
Start out with a
boxelement. A1 x 1 x 1m box is built by default. -
Edit the size of the box in settings:
Name Element type Center point [m] Size [m] Rotation [deg] box Box X: 0X: 24e-3X: 0Y: 0Y: 2e-3Y: 0Z: 0Z: 3e-3Z: 0 -
Rebuild the box with correct dimensions.
-
Confirm model changes before moving on.
Step 2 - Define shared regions
Section titled “Step 2 - Define shared regions”-
Go to the
Commonsidebar. -
Define shared regions:
Name Region type Target clampSurface X direction bottom surface ( 1)topSurface Z direction top surface ( 6)
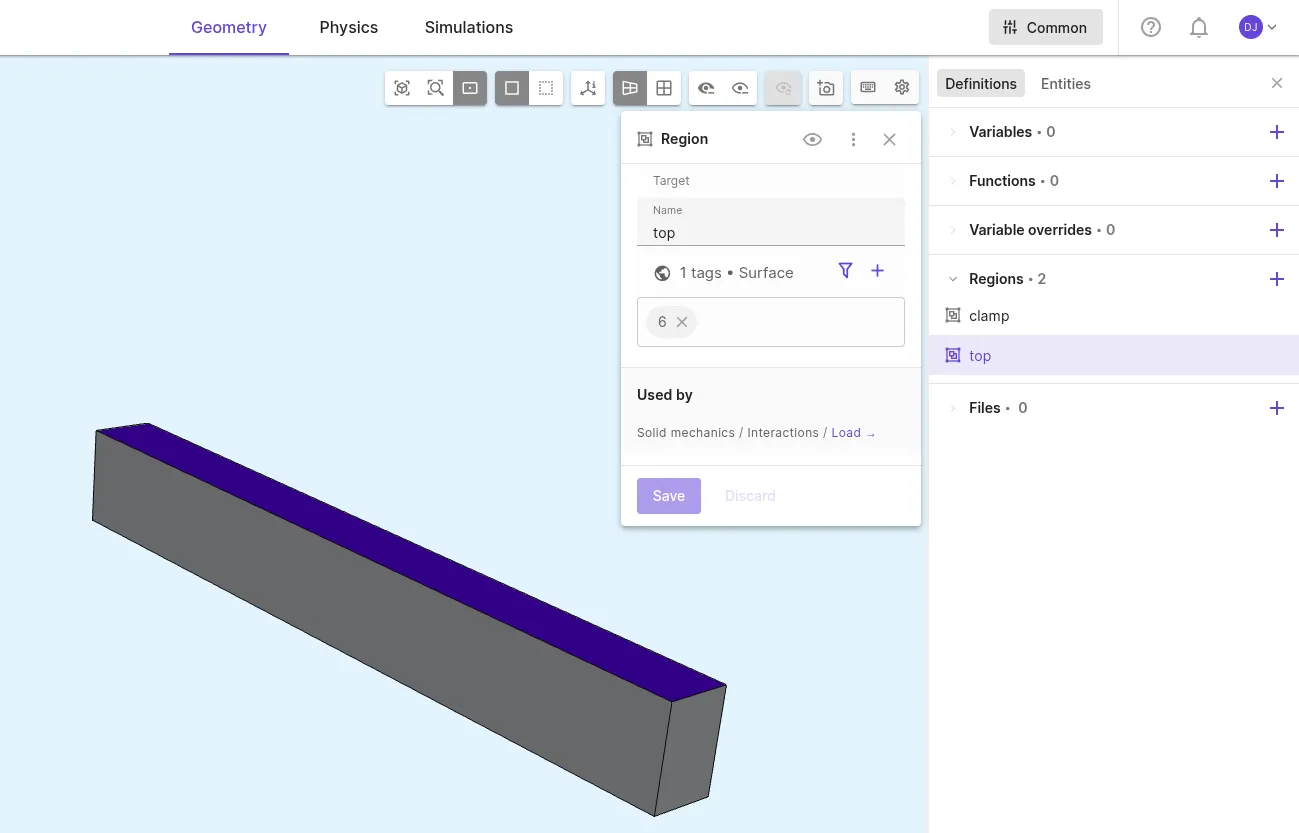
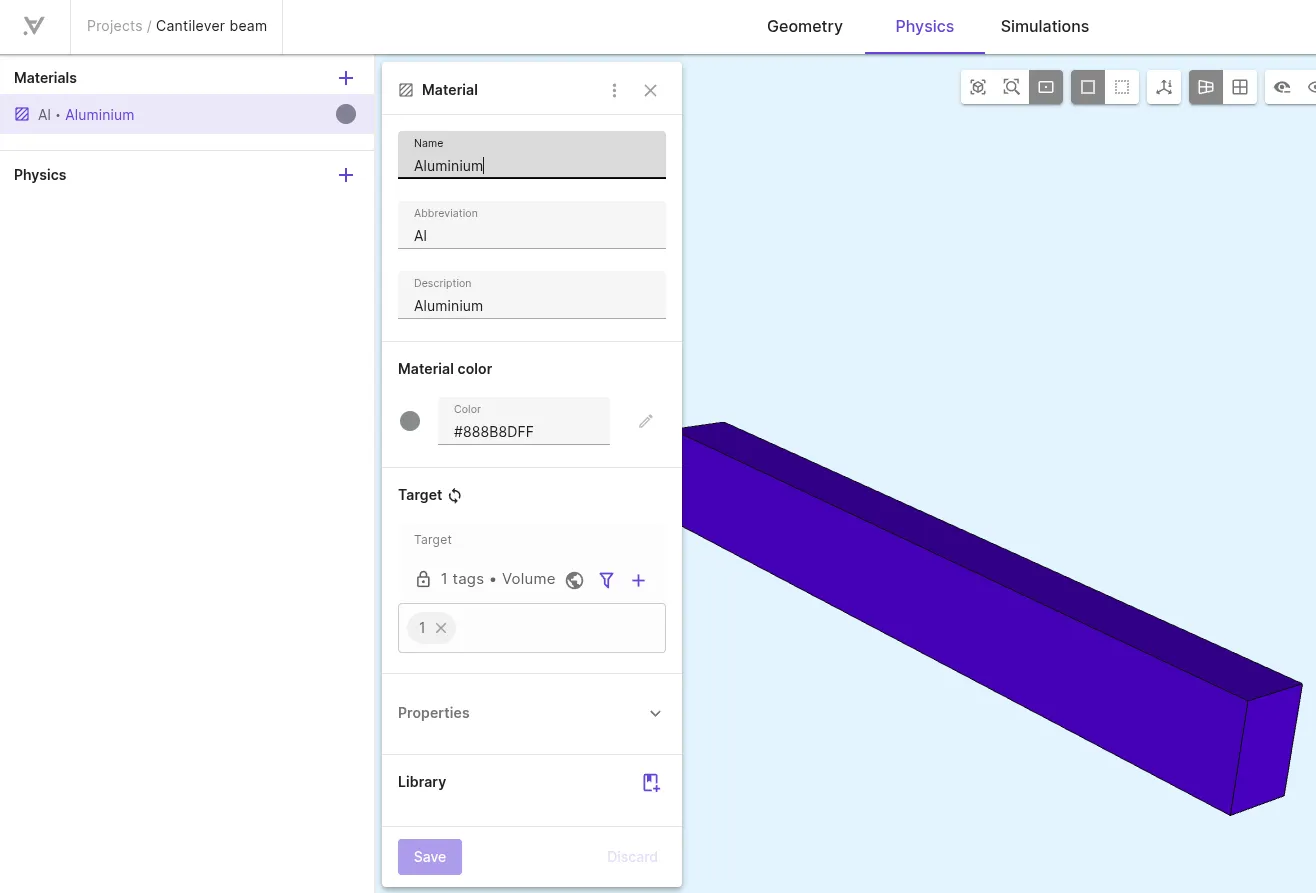
Step 3 - Define the material
Section titled “Step 3 - Define the material”Assign the predefined Aluminium material to the beam volume (1).
Step 4 - Define the physics & boundary conditions
Section titled “Step 4 - Define the physics & boundary conditions”-
Go to the
Physicssection. -
Add the
Solid mechanicsphysics.Not selecting a target for a physics makes it default to the whole model. Let solid mechanics target default to the beam volume.
Physics Target Solid mechanics Beam (volume 1) -
Add a
Clampinteraction to Solid mechanics.Name Interaction type Target Clamp Clampclampshared region (surface1)This boundary condition will constraint all components of the displacement vector in the targeted region to zero displacement: , , .
-
Add a
Loadinteraction to Solid mechanics.Name Interaction type Target Value [X; Y; Z] Load Loadtopshared region (surface6)[0; 0; -1000]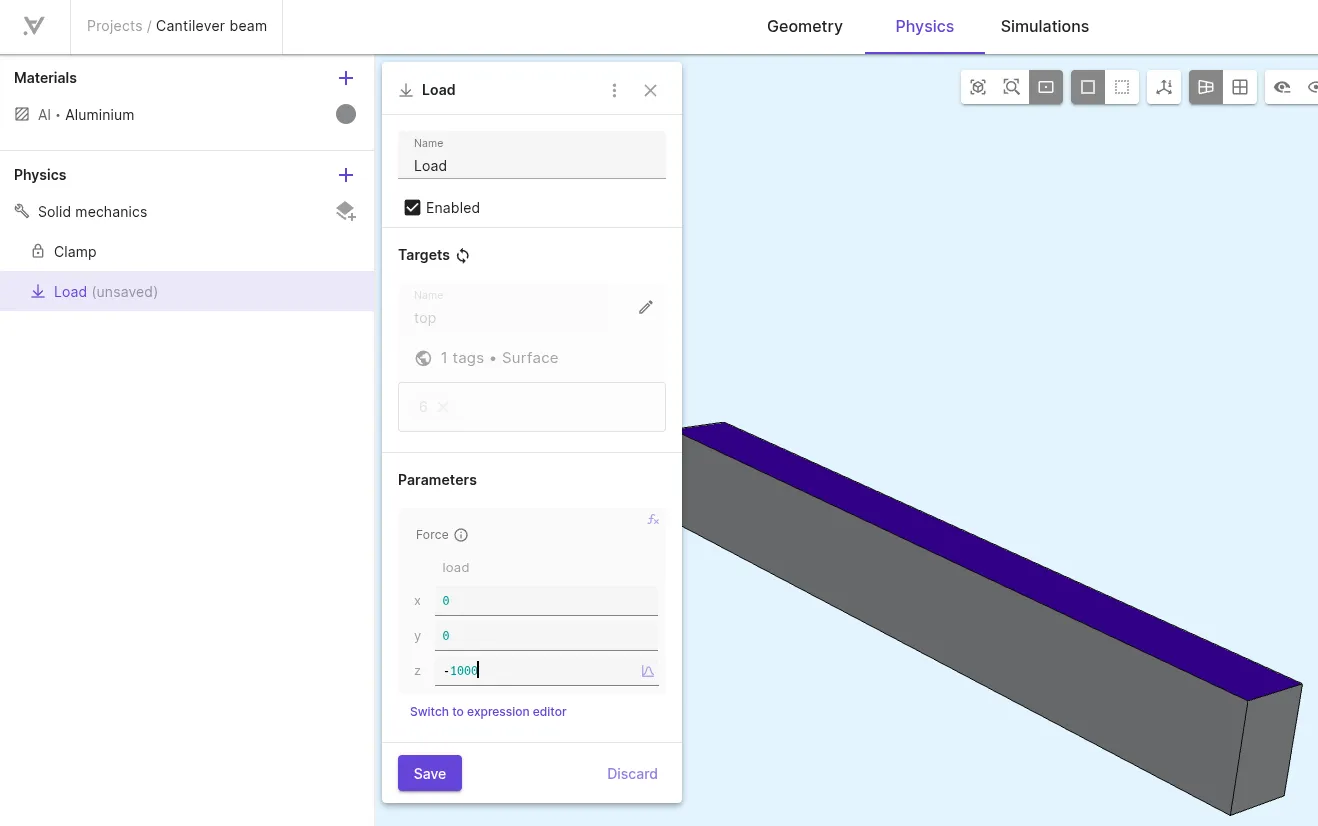
Step 5 - Generate the mesh
Section titled “Step 5 - Generate the mesh”-
Proceed to the
Simulationssection. -
Generate a new mesh with default settings and check the preview.
Step 6 - Apply simulation settings & run
Section titled “Step 6 - Apply simulation settings & run”-
Create a new simulation.
-
Set Analysis Type to
Static. -
Select the mesh you generated as the mesh for your simulation.
-
Add the displacement field output
u. -
Run the simulation.
Step 7 - Visualize results
Section titled “Step 7 - Visualize results”-
Add a visualization for the
ufield. -
Add
Warpto the visualization and activate it. -
Click on the Refresh icon next to Warp scale factor.
-
Render the deformed geometry scaled up according to the scale factor.
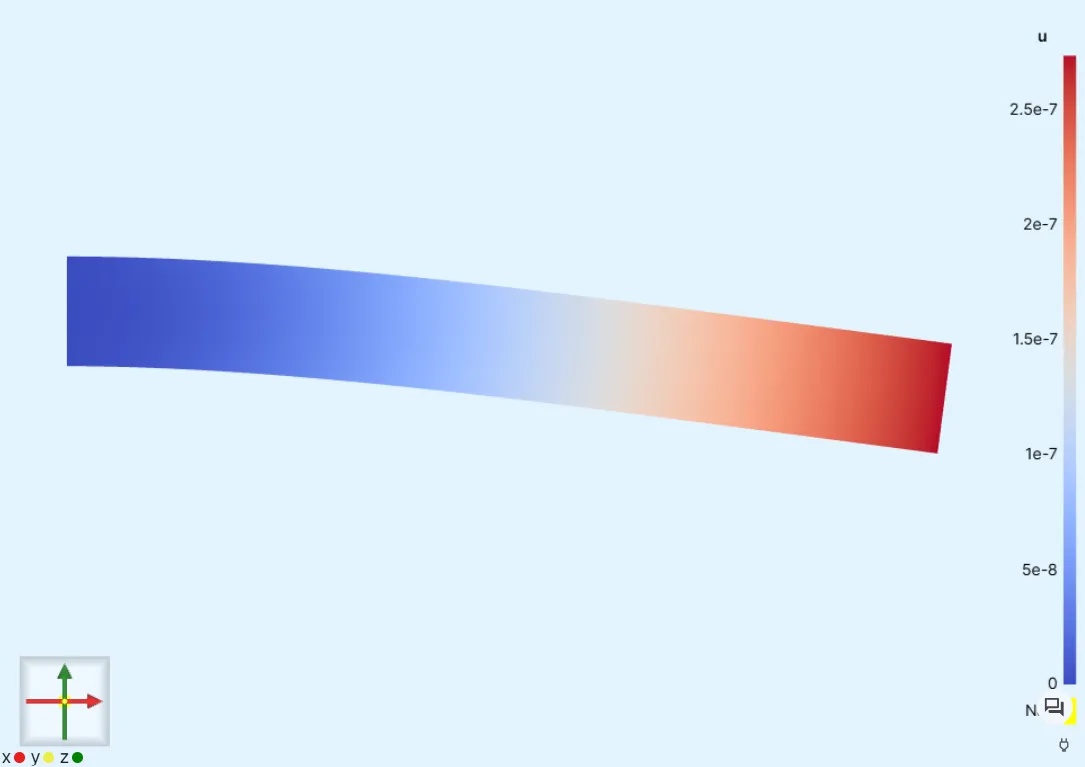
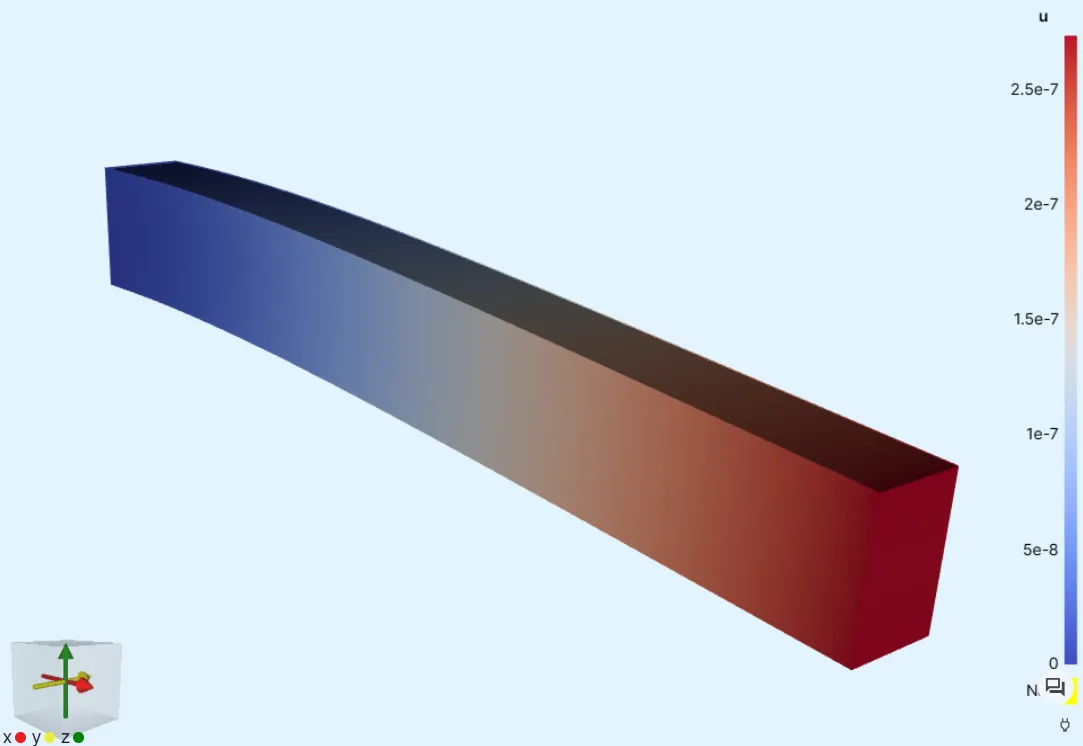
Here, the scale factor is
8772.